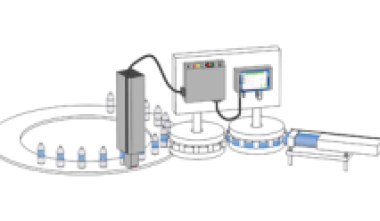
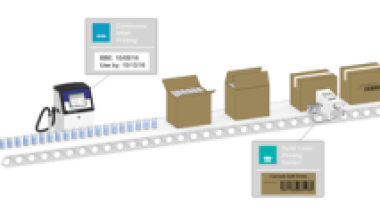
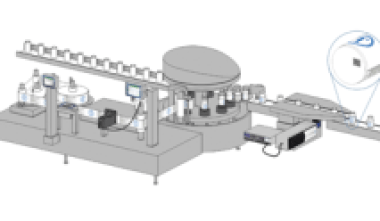
Date coders are machines that print various best before and expiry date information onto products, packaging and labels. Date coding of products – especially food, beverage and pharmaceutical products – is required by Kenyan regulations. Manufacturers also need marks, such as production date codes and batch codes, for their own internal tracking of production and logistics to ensure that products are shipped promptly to market. The date that a product is manufactured often determines a its expiration date, which is required to be prominently displayed on certain food, beverage and pharmaceutical packaging and labelling.
Most date coding printers today are automatic machines, incorporating software programmed to automatically generate and apply date codes on large volumes of products. Many date coders are used on high-speed production lines where codes are applied at high line speeds, requiring them to be able to maintain high print quality while printing on moving products and packages. On some production line date coders, line operators manually generate Julian date codes at the beginning of each day’s shift.
Date Coding Machines
Date coders use various printing and marking technologies. Most common date coding machine types include: continuous inkjet, thermal inkjet, laser marking, thermal transfer, or print and apply labelling technology to print codes on products.
In continuous inkjet date printing systems, a stream or jet of ink passes through a nozzle in the printhead. A piezoelectric resonator vibrates to ensure that the jet is broken up into uniform, single drops. A charge electrode is attached near the break-up point of the ink. Each drop that detaches from the jet is proportional to the applied voltage charge. The charged droplets then pass between two baffles as a high constant voltage runs between these two elements. This ensures that the ink droplets reach the substrate in exact location to complete the code being printed in clear, readable condition. Continuous inkjet inks are available with various properties to print codes with the ideal adhesion, colour, opacity, and solvent type for the product or package’s surface.
Thermal inkjet printers fire tiny ink drops onto packaging as the package passes by a printhead. These ink drops are propelled out of one or more rows of fine-gauge nozzles by the rapid cycling of a small resistor underneath each nozzle. The resistors boil a small amount of ink, creating a small steam bubble that propels the ink drop. Thermal inkjet printing is inherently clean and the printheads are relatively small, aiding integration into packaging lines where pace is limited. Dry times of less than one second are achievable, speeding production and reducing the risk of smeared and/or unreadable codes.
In contrast to inkjet printers, laser coders use a focused beam of light to etch or physically alter the top layer of a substrate. The beam of light is steered by two mirror galvanometers that direct the laser beam in two planes, creating the date code on the product or package surface.
Thermal transfer overprinters are often mounted onto labelers on production lines to print variable high-resolution data, including date codes, directly onto a label immediately before application onto products moving down a packaging line.
Print and apply labelling systems employ a thermal transfer printer that prints by transferring characters from a ribbon to the label surface, after which the label is applied to a passing product or package. This process can be achieved with various application methods including direct, tamp and corner wrap.
To determine which date coding equipment is best for a particular production line, companies must weigh various factors, including the kind of substrate the codes will be printed on, the production line speed, the stability of product and package handling on the line, space availability for installation of the code printer, and purchase and operational costs.
Date Coding Equipment Solutions

Continuous Inkjet Printers (CIJ)
Reliable, fast industrial inkjet batch coders with Videojet ink formulations to print on almost any product packaging material – including food grade and UV inks.

Laser Coder Machines
Lasers can deliver high resolution, robust batch codes, linear and 2d barcodes – and are suitable for a wide range of product coding applications.

Thermal Inkjet Coders (TIJ)
High resolution coding solution ideal for track & trace and serialisation requirements, such as those in the pharmaceutical industry.
Categories
Contact Us
New Equipment Sales:
+254-701-373789